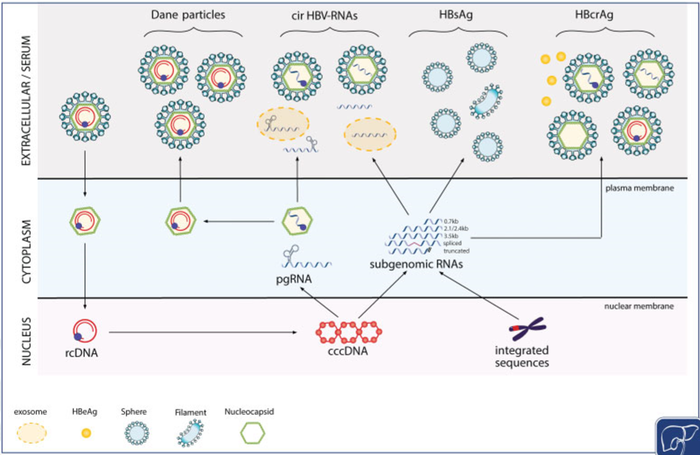
The goals of the CirB-RNA project are the validation of circulating hepatitis B (HBV) RNAs as an innovative, clinically relevant, non invasive biomarker for patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) to predict a functional cure and the development of the related diagnostic test.
The 257 million chronic HBV infections remain a major health burden worldwide. Only 1.7 million patients are currently treated for their infection. However, this pathology can lead to chronic liver inflammation, cirrhosis or even to hepatocellular carcinoma, the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the world. Current treatments for chronic hepatitis B include pegylated interferon alpha2a and nucleos(t)ide analogues (NUC). Only a limited number of treated patients achieve the loss of hepatits B surface antigen (HBsAg) that defines a functional cure of HBV infection allowing treatment cessation and is associated with a decreased risk of liver complications.
A key challenge for drug development is to target the pool of cccDNA, the nuclear replicative intermediate that acts as template for the transcription of all viral mRNAs. Several new drugs have reached the preclinical and/or clinical evaluation with the aim of silencing cccDNA and/or reducing the size of the cccDNA pool to achieve a functional cure with finite treatment duration.
The working hypothesis is that cirB-RNAs reflects the transcriptional activity of the cccDNA in the liver and would be the best biomarker for the reduction of the cccDNA pool and it functional inactivation. The goals of the CirB-RNA project are first the validation of the circulating hepatitis B RNAs as an innovative, clinically relevant and non invasive biomarker to predict a functional cure ; and second the development and validation of the related diagnostic test.
2023 Apr -
Journal of Hepatology
A 3-year course of bulevirtide monotherapy may cure HDV infection in patients with cirrhosis
Maria Paola Anolli et al.
2019 Jul -
Antiviral Research
Non-invasive biomarkers for chronic hepatitis B virus infection management
Caroline Charre et al.
Institut d’hépatologie de Lyon, 2023