Accueil » Hepatocellular carcinoma
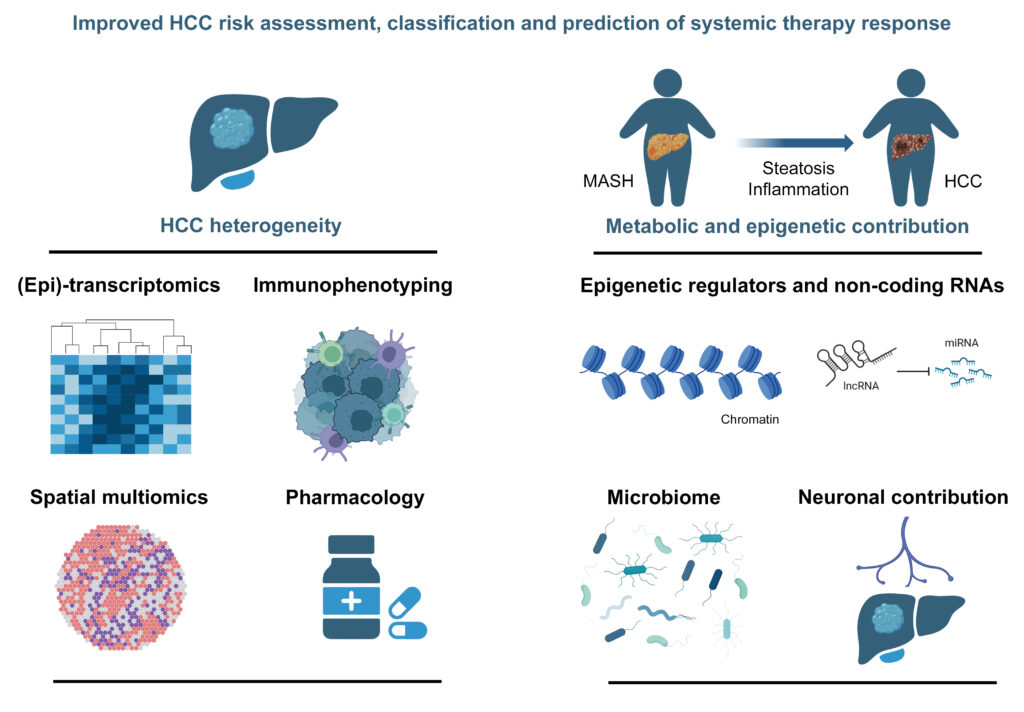
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. The majority of HCCs is associated with chronic liver disease due to chronic viral hepatitis, excessive alcohol intake, and metabolic diseases. Although common mechanisms and pathways involved in HCC development have been described for these etiological factors, HCC is an extremely heterogenous cancer. Importantly, treatment of the underlying cause, e.g., inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication or eradication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) reduces but does not eliminate the risk of HCC development; thus HCC incidence continues to rise globally. Curative treatments are limited to patients with early-stage disease. Patients with advanced disease can benefit from systemic treatments but only a proportion of patients respond, and the clinical outcome of HCC remains overall dismal.
No results found.
2023 Sep -
Liver Int.
PMID : 37402699
Axon guidance molecules in liver pathology: Journeys on a damaged passport.
Chicherova I, Hernandez C, Mann F, Zoulim F, Parent R.
2021 Apr -
J Clin Med.
PMID : 36207612
Host Epigenetic Alterations and Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Clin Med.
Zeisel et al.
2022 Nov -
Hepatology
PMID : 35253915
Hepatic inflammation elicits production of proinflammatory netrin-1 through exclusive activation of translation
Barnault et al.
2020 Nov -
Gut
PMID : 32114505
Hepatitis B protein HBx binds the DLEU2 lncRNA to sustain cccDNA and host cancer-related gene transcription
Salerno et al.
2024 Feb -
Cancers (Basel)
PMID : 34206504
The lncRNAs in HBV-Related HCCs: Targeting Chromatin Dynamics and Beyond.
Alfano et al.
2018 Nov -
Viruses
PMID : 30380697
Non-Coding RNAs and Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Plissonnier et al.
2018 Nov -
J Hepatol
PMID : 30193922
Dietary exacerbation of metabolic stress leads to accelerated hepatic carcinogenesis in glycogen storage disease type Ia
Gjorgjieva et al.
Institut d’hépatologie de Lyon, 2023