Accueil » Liver Metabolism – MASLD
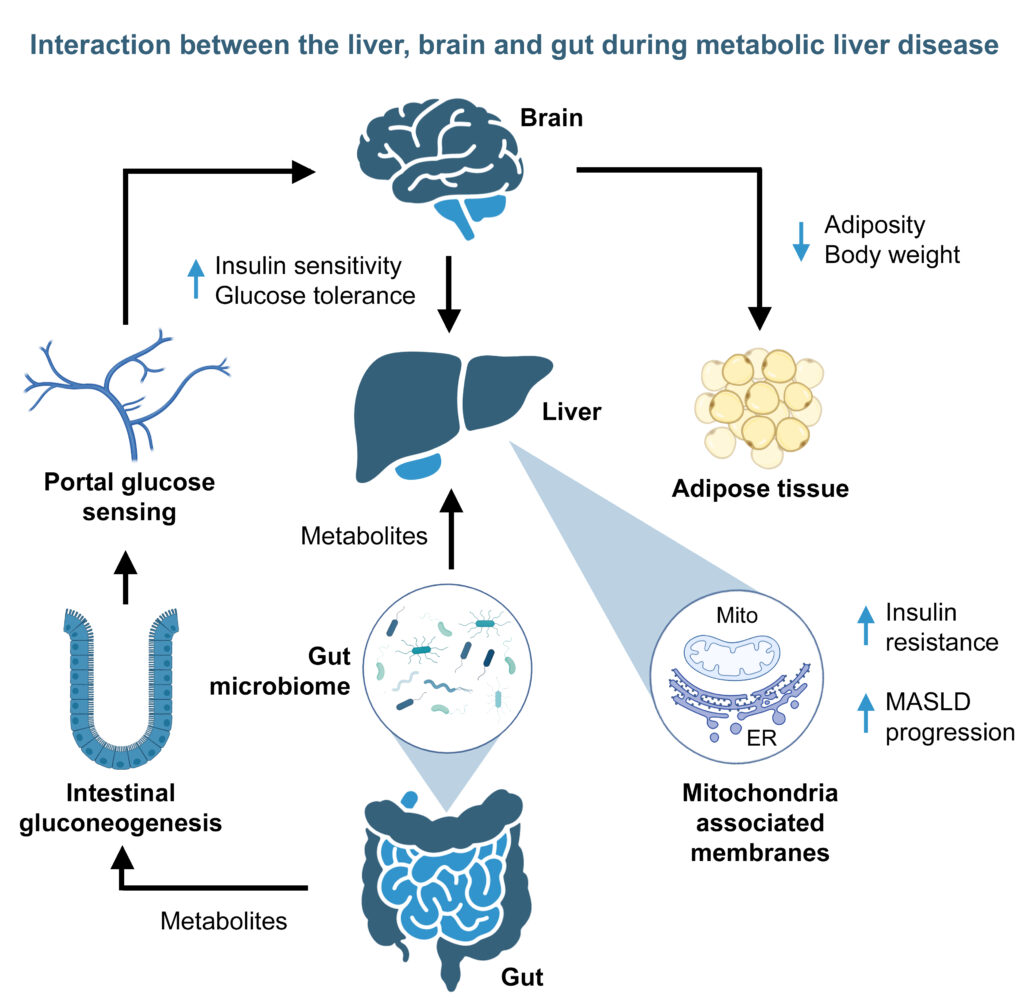
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver pathology and a leading cause of liver-related morbidity and mortality. MASLD is defined by the presence of hepatic steatosis (fat deposition) in conjunction with at least one cardiometabolic risk factor (e.g., type 2 diabetes, hypertension or overweight) and no other discernible cause. High-calorie diets and sedentary lifestyles drive the development and progression of MASLD and its increasing prevalence is projected to results in a 2- to 3-fold increase in the burden of cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease (ESLD) by 2030. In a significant minority of cases, MASLD progresses from hepatic steatosis to metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH) with lobular inflammation, hepatocyte injury and progressive fibrosis, which may lead to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and ESLD. Metabolic comorbidities, environmental influences, genetic and epigenetic factors increase the risk of MASLD progression.
The overall goal of this clinical and translational research program is to study:
using an integrative approach to study the transition of cellular states from MASLD, liver steatosis, MASH and liver fibrosis to HCC.
No results found.
2023 Jun -
Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes
PMID : 37312899
Comparison of Pathway Referrals for Liver Fibrosis Risk Stratification Performed in Diabetology and Nutrition Clinics.
Caussy et al.
2023 Sep -
Cell Calcium
PMID : 37506596
Calcium signalling in hepatic metabolism: Health and diseases
Humbert et al.
2023 Nov -
Liver Int
PMID : doi: 10.1111
Dual alcohol and metabolic-related liver disease: Results from a population of liver transplant patients
Erard, Villeret et al.
2023 Jan -
Commun Med (Lond)
PMID : 36596859
A multistakeholder approach to innovations in NAFLD care
Schattenberg et al.
2023 Sep -
Diabetes Metab
PMID : 34363981
Management of diabetes mellitus in patients with cirrhosis: An overview and joint statement
Boursier et al.
2022 Sep -
J Hepatol.
PMID : 35358616
Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria miscommunication is an early and causal trigger of hepatic insulin resistance and steatosis
Beaulant et al.
Institut d’hépatologie de Lyon, 2023